Mar
1
From User Need to Market Saturation The Product Lifecycle Considerations for Long-Term Dominance
Imagine walking down a road, looking at some cocoons hanging on the tree above you. They’re diligently consuming leaves, while building strength. This parallels the early stage of gathering resources & deciding the core features. The metamorphosis into a cocoon reflects the refinement a product undergoes where feedback & testing make it into a market fit.
Like a butterfly, a product too blossoms in its growth stage, while expanding its reach and value proposition.
From anticipating challenges to continuous evolution, businesses should leverage this example to navigate their unique product’s development. By understanding these stages of dynamicity, businesses adapt, increasing their chances of gaining success.
Well, a product lifecycle refers to stages like these that play vital roles in the development of any software or application. By segmenting the entire lifetime of a product, businesses can achieve an in-depth understanding of customers, resulting in more market-relevant products.
What- PLM?
The term ‘Product Lifecyle’ doesn’t justify the myriad of tasks and decisions that fall under it. From initial ideation to calls with dev teams; from getting critical user feedback to gathering updated data- every byte of information collected in this product lifecycle makes or breaks the success of the product.
The act of Product Lifecycle Management is the method of managing the dynamic journey of a product in the market, from inception to conclusion.

To make this method efficient, there are only a couple of things businesses need to focus on, namely user demands & specific niches in the huge sea of customers.
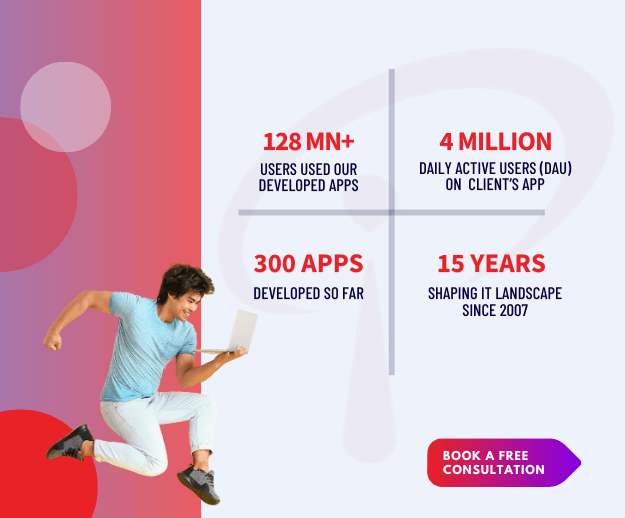
You know, the global market for PLM is said to reach $120 billion by 2030, at a growing CAGR of 7.7%. This shows that more industries are adopting PLM strategies across the world.
These numbers provide a unique opportunity for you to explore more about PLM and how it has provably helped businesses scale up.
So- stop researching! Read the article below to know more about the pivotal PLM and its extended uses in development!
From User Needs to Market Saturation
Understanding user needs is like throwing straight hoops in the basketball ring. You win every single game. These insights act as a guidepost for your business to create market fit solutions & services, bridge real market gaps, and ultimately, win hearts. (and wallets!)
It’s important to understand the ‘why’ behind their actions, to figure out the scratch your products need to itch.
Let’s look at a leading example that paid attention to user needs, enabling them to find their huge target audience in saturated markets.
Dyson
Dyson’s founder, James Dyson, reinvented the market for vacuum cleaners. The company is killing it in today’s market, and what wonders are their products! (Ask any girl about the Dyson Airwrap!)
To achieve fulfilling demand, James invested a lot in research and development, both for his products & scalability of the company. As a result, Dyson is one of the leading companies in the world, trusted by millions of users, covering different industries like beauty, retail & home tech all at once.
Let’s understand their strategic approach today.
A. Idea Generation & Development
1. User Centricity: James recognized the limitations in conventional vacuum cleaners. Bulky machines with clogged bags & reducing suction frustrated users a lot.
He fully reimagined the vacuum cleaner by addressing unmet user needs such as powerful suction, ease of use, and increasing hygiene by inventing cyclone technology & bagless designs.
2. Rapid Prototyping & Testing: Dyson invests heavily in developing in-house capabilities for testing & prototyping. This enables iterative designing, and products that evolve quicker based on user feedback & performance.
3. Focusing on Core Technologies: The company enables continuous innovation & differentiation through R&D in their core technologies such as cyclone technology & digital motors.
B. Production & Supply Chain Management
1. Vertical Integrations: By owning significant portions of its manufacturing, Dyson has greater control over its quality & flexibility in production. This also helps them to react to changes instantaneously.
2. Agile Manufacturing: To minimize waste and gain efficiency, Dyson uses flexible processes that adapt quicker to changes in design or demand iteratively.
C. Post-Launch & End-of-Life activities
1. Customer Support: through comprehensive customer service, Dyson fosters customer loyalty & repeat purchases.
2. Software Updates & Improvements: Dyson extends its products’ functionality and lifecycles through regular software updates.
3. Recycling: Dyson contributes to circular economy by organizing programs for recycling old Dyson products.
Impact of following a PLM-based strategy
1. Reduced time-to-market:
Engaging in agile processes through a user-centric approach helped Dyson capitalize on market trends & evolving user needs. This enabled quicker product launches through series of iterations.
2. Quality deliverables
Vertical integrations and rigorous testing ensured high-quality products that delivered superior performance, one product at a time.
3. Enhanced brand reputation
A focus on user experience created a positive brand image, with customer loyalty & advocacy for Dyson.
How did PLM influence Dyson’s strategies?
Dyson’s PLM went beyond traditional practices through integration of user needs, research, technology & sustainability at each stage. This holistic approach resulted in all stages contributing to creating user-centric & innovative products.
But the impact of PLM goes far ahead from Dyson’s success story.
From technology giants to retail manufacturers, companies throughout different industries have reaped substantial benefits by implementing an effective PLM strategy.
- 1. Treat user needs as the driving force, not an afterthought, to gain a loyal customer base.
- 2. Innovation powers up differentiation, Businesses should invest more in R&D and new technologies to offer unique value propositions & stand unique in the market.
- 3. Vertical integration & collaboration bring control, efficiency & high responsiveness.
- 4. Businesses should actively seek user feedback, performance data & benchmarks against industry giants to continue ongoing refinement & adaptability.
Remember, it’s not about having the latest tech or biggest budget, it’s about creating specialized experiences where user needs, innovation & sustainability concerns are attuned to the development process.